Details for: ACTEMRA - COVID-19
Company: HOFFMANN-LA ROCHE LIMITED
| DIN | DIN name | Active Ingredient(s) | Strength | Dosage Form | Route of Administration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02350092 | ACTEMRA | TOCILIZUMAB | 80 MG / 4 ML | SOLUTION | INTRAVENOUS |
| 02424770 | ACTEMRA | TOCILIZUMAB | 162 MG / 0.9 ML | SOLUTION | SUBCUTANEOUS |
| 02483327 | ACTEMRA | TOCILIZUMAB | 162 MG / 0.9 ML | SOLUTION | SUBCUTANEOUS |
| 02350106 | ACTEMRA | TOCILIZUMAB | 200 MG / 10 ML | SOLUTION | INTRAVENOUS |
| 02350114 | ACTEMRA | TOCILIZUMAB | 400 MG / 20 ML | SOLUTION | INTRAVENOUS |
Consumer Information
This information was provided by the drug’s manufacturer when this drug product was approved for sale in Canada. It is designed for consumers and care givers. It is a summary of information about the drug and will not tell you everything about the drug. Contact your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions about the drug.
What the medication is used for
ACTEMRA treatment should be initiated and supervised by specialist physicians experienced in the
diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and familiar with the ACTEMRA efficacy and
safety profile.
ACTEMRA (also known as tocilizumab), is a medicine that is used to treat adults with moderate to
severe rheumatoid arthritis and adults with giant cell arteritis (GCA). ACTEMRA is also used to treat
active systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) and polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA) in
patients aged 2 and above. It is also used to treat people who experience severe or life-threatening
cytokine release syndrome (CRS) following chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell treatment, in patient
populations specified for authorized CAR T cell products.
ACTEMRA is used to treat hospitalized adults with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) who are
receiving systemic corticosteroids and require oxygen support.
The safety and efficacy in patients aged less than 2 years in pJIA and sJIA has not been established.
The safety and efficacy in patients aged less than 3 years in CRS has not been established.
The safety and efficacy of ACTEMRA in children with RA and GCA conditions has not been established.
What it does
ACTEMRA is a medicine that helps keep the immune system from attacking healthy tissues in the body.
A normal immune system leaves healthy body tissues alone. In people with rheumatoid arthritis, the
immune system attacks normal body tissues causing damage and inflammation, especially in the
tissues of your joints. ACTEMRA interferes with an important step in this attack (blocks a cytokine
called IL-6 which is found at high levels in the joints affected by rheumatoid arthritis). By decreasing
the immune system’s attack on normal tissues, ACTEMRA can reduce pain, joint inflammation and
tiredness leading to a better quality of life.*
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a protein that is made by the immune system and the body uses IL-6 to manage
infections. It also plays a major role in the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). People
with RA have too much IL-6.
When it should not be used
Do not use ACTEMRA if:
- you are allergic to tocilizumab or any other non-medicinal ingredient in ACTEMRA
- you have an active infection or active liver disease.
What the medicinal ingredient is
Medicinal ingredients: tocilizumab
What the non-medicinal ingredients are
Non-medicinal ingredients:
Intravenous formulation – Disodium phosphate dodecahydrate, polysorbate 80, sodium dihydrogen
phosphate dihydrate, sucrose, water for injections.
Subcutaneous formulation – L-arginine, L-arginine hydrochloride, L-histidine, L-histidine hydrochloride
monohydrate, L-methionine, polysorbate 80, water for injections.
What dosage form it comes in
Intravenous infusion: available in vials containing of 80, 200 or 400 mg of tocilizumab.
Subcutaneous injection: supplied in either a single-use pre-filled syringe, or a single-use
Autoinjector,
each containing 162 mg of ACTEMRA in a 0.9 ml volume. The prefilled syringe is not made with natural
rubber latex.
Warnings and precautions
Serious Warnings and Precautions
Serious Infections
Some serious infections have been observed with the use of ACTEMRA. These infections include:
active tuberculosis (TB), bacterial, viral and fungal infections. Most patients who developed these
infections were taking other drugs that lower the immune system. Hospitalization or death associated
with these infections have been reported. Ensure you tell your doctor if you are taking any other
medication.
ACTEMRA should not be started if you have any active infections including long-term or localized
infections. If a serious infection develops, stop ACTEMRA until the infection is controlled.
Your doctor will evaluate you for both active and non-active tuberculosis before starting treatment
with ACTEMRA. During and after treatment with ACTEMRA, you will be closely monitored for signs and
symptoms of an infection, including the possible development of tuberculosis even if you tested
negative prior to initiating therapy.
Hepatotoxicity
Serious cases of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) have been observed in patients treated with
ACTEMRA. Some of these cases have resulted in acute liver failure requiring a liver transplant.
To help avoid side effects and ensure proper use, talk to your healthcare professional before you take ACTEMRA. Talk about any health conditions or problems you may have, including if:
- You have ever had a bad reaction to tocilizumab or any of the non-medicinal ingredients.
- You are allergic to other medications, food or dyes.
- You are taking any other medications, including but not limited to corticosteroids. You can take other medicines provided your doctor has prescribed them and has told you it is ok to take them while you are taking ACTEMRA. You should also tell your doctor about any over-the-counter drugs, herbal medicines and vitamin and mineral supplements you are taking.
- You have any kind of infection, or if you often get infections. Treatment with ACTEMRA could cause your infection to get worse. Tell your doctor immediately if symptoms from an infection occur (see warning box above)
- You have diabetes, HIV/AIDS or a weaker immune system, which can increase your risk of serious infections.
- You live or have lived, or have travelled to certain parts of the world where there is an increased chance for getting certain kinds of fungal infections (histoplasmosis, coccidiomycosis, or blastomycosis). These infections may happen or become more severe if you use ACTEMRA.
- You are scheduled to have surgery.
- You have recently had a vaccination or are planning to have a vaccination. You or your child should be brought up to date (if possible) on all recommended vaccinations, prior to initiation of therapy with ACTEMRA. Certain vaccines should not be given while receiving ACTEMRA.
- You have tuberculosis (TB), or if you have been in close contact with someone who has had TB. Your doctor should test you for TB before starting treatment with ACTEMRA.
- You have hepatitis or any disease of the liver.
- You have had any type of cancer
- You have disease of the nerves or nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis
- You have a history of macrophage activating syndrome (MAS), a rare but serious immune reaction in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
- You have abdominal pain or have been diagnosed with stomach, pancreas or bowel (intestine) problems, including ulcers, inflammation or infection, including diverticulitis and pancreatitis
- You have cardiovascular risk factors such as high blood pressure and raised cholesterol levels.
Other warnings you should know about:
Pregnancy Registry: A pregnancy registry has been established to monitor the outcomes of pregnant
women exposed to ACTEMRA. Women who become pregnant while taking ACTEMRA are encouraged
to register themselves by calling 1-877-311-8972.
ACTEMRA should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to
the fetus. Women who could become pregnant need to use effective birth control methods during
ACTEMRA treatment and for at least 3 months after treatment with ACTEMRA.
Tell your healthcare professional about all the medicines you take, including any drugs, vitamins,
minerals, natural supplements or alternative medicines.
Interactions with this medication
The following may interact with ACTEMRA:
- Biological medicines: etanercept injection, etanercept for injection, adalimumab injection, infliximab powder for solution, rituximab injection, rituximab for injection, abatacept for injection, abatacept injection, anakinra injection, golimumab injection, golimumab for injection, certolizumab pegol injection. ACTEMRA has not been studied in combination with these biological medicines. ACTEMRA is not to be used with biological medicines that are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Proper use of this medication
Before starting treatment, make sure your doctor knows if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines (including those you have bought for yourself from a pharmacy, supermarket or health store). This is extremely important, as using more than one medicine at the same time can strengthen or weaken their effect. ACTEMRA should not be used with other drugs unless your doctor has told you it is safe to do so.
How to take ACTEMRA:
- The JointEffort® program has been established to facilitate the administration of ACTEMRA. Information about the JointEffort® program can be obtained by calling 1-888-748-8926.
Usual Dose:
Intravenous formulation:
The recommended starting dose of ACTEMRA for adult patients with RA is 4 mg per kg of body weight
with an increase to 8 mg per kg of body weight, based on how you respond to the drug.
ACTEMRA will be given to you by a healthcare professional using an intravenous line. This means the
medicine will be given to you through a needle placed in a vein in your arm. It will take about 1 hour to
give you the full dose of medicine.
ACTEMRA should be given once every 4 weeks. Your doctor will advise you on how long you will
continue to be treated with ACTEMRA.
The recommended dose for children with sJIA is either 8 or 12 mg per kg of body weight depending on
the child’s weight. Children with sJIA receive a dose of ACTEMRA every 2 weeks.
The recommended dose for children with pJIA is either 8 or 10 mg per kg of body weight depending on
the child’s weight. Children with pJIA receive a dose of ACTEMRA every 4 weeks.
The recommended dose of ACTEMRA for CRS patients is 8 mg for every kg of body weight if you weigh
30 kg or more or 12 mg for every kg of body weight if you weigh less than 30 kg. ACTEMRA can be given
alone or in combination with corticosteroids.
The recommended dose of ACTEMRA for treatment of adult patients with COVID-19 is a single 60-
minute infusion of 8 mg per kg of body weight. A second dose may be needed.
Subcutaneous formulation:
The recommended starting dose of ACTEMRA for an adult patient with RA is 162 mg given once every
other week followed by an increase to every week depending on clinical response. Patients weighing
100 kg or more should receive treatment weekly.
For adult patients treated for GCA, the ACTEMRA dose is 162 mg given once every week as a
subcutaneous injection. In some cases, your doctor may tell you to take 162 mg of ACTEMRA once
every other week. Your doctor will also ask you to take glucocorticoids with ACTEMRA. Your doctor
may eventually tell you to stop taking glucocorticoids and use ACTEMRA alone.
The recommended dose for children with pJIA is 162 mg either every two or three weeks depending on
the child’s weight.
The recommended dose of ACTEMRA for patients with sJIA is:
- 162 mg once every two weeks for patients below 30 kg,
- 162 mg once every week for patients ≥ 30 kg
The pre-filled syringe can be used to treat children of all approved ages. The autoinjector should not be
used to treat children < 12 years of age.
“Subcutaneous” means that it is given into the fat layer just under the skin. The recommended
injection sites are the abdomen, thigh and upper arm. The sites should be rotated and injections should
never be given into moles, scars, or areas that are tender, bruised, red, hard or have open sores.
Your healthcare provider should show you how to prepare and inject properly before you use the
ACTEMRA subcutaneously for the first time. Ask your healthcare provider any questions you may have.
Do not attempt to administer an injection until you are sure you understand how to inject using the
pre-filled syringe or a single-use autoinjector. Appendix 1 - Instructions for Use explains the use of both
the pre-filled syringe and the autoinjector. It is important that you follow the specific instructions for
using the kind of ACTEMRA that your doctor has prescribed.
Overdose:
Because ACTEMRA is given intravenously by a doctor or nurse, and the subcutaneous injection comes in a single-use pre-filled syringe or autoinjector, it is unlikely that you will be given too much. However, if you are worried then talk to your doctor. If necessary, you will be monitored closely for any signs and symptoms of overdose and be treated for those symptoms as necessary.
Missed Dose
If you have missed your dose of ACTEMRA, ask your doctor when to schedule your next dose.
Side effects and what to do about them
These are not all the possible side effects you may have when taking ACTEMRA. If you experience any
side effects not listed here, tell your healthcare professional.
The most common side effects of ACTEMRA are upper respiratory tract infections (common cold, sinus
infections) headaches, and increase in blood pressure.
In pJIA the most common side effects of ACTEMRA were upper respiratory tract infections, nausea,
headache dizziness, decrease in blood pressure and rash. Patients with pJIA receiving ACTEMRA
subcutaneously also experienced reactions at the injection site.
Possible serious side effects include serious infections, liver injury and allergic reactions.
Patient advice regarding early recognition and treatment to limit risk of a serious infection.
Be alert for the first signs of infection such as:
- body aches, fever, chills
- cough, chest discomfort/tightness, shortness of breath redness, heat, unusual swelling of skin or joint
- abdominal pain/tenderness and/or change in bowel function
Call your doctor and seek medical attention without delay if you think you might be developing an
infection.
A severe skin reaction called Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and serious drug-induced liver injury
(DILI), including rapid loss of liver function, inflammation of the liver and jaundice (yellowing of skin and
eyes) were reported during treatment with ACTEMRA.
Stop taking ACTEMRA and call your doctor or seek medical attention immediately if you notice any of
the following:
- Difficulty with breathing or light-headedness.
- Rash, itching, hives, swelling of the lips or other signs of an allergic reaction.
- Chest pain.
- Feeling dizzy or faint.
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark brown coloured urine, pain or swelling in the upper right side of the stomach area, or you feel very tired and confused.
Patient advice regarding hypersensitivity reactions (also known as anaphylaxis, if severe)
If you develop symptoms such as, but not limited to skin rash, itching, chills, swelling of face, lips,
tongue or throat, chest pain, wheezing, difficulty breathing or swallowing or feeling dizzy or faint at any
time following an injection, you should seek emergency care immediately.
Since this medicine can cause dizziness, it is recommended that you do not drive or use machines until
it has stopped.
Tell your doctor as soon as possible if you notice any of the following: signs of infection such as fever
and chills, mouth or skin blisters, stomach ache or persistent headaches.
The symptoms described above can be signs of the side effects listed in the table below, all of which
have been observed with ACTEMRA in controlled clinical trials:
| Symptom / effect | Talk to your healthcare professional Only if severe | Talk to your healthcare professional In all cases | Stop taking drug and get immediate medical help |
|---|---|---|---|
| VERY COMMON | |||
| For sJIA (SC formulation): Injection Site Reactions like redness of the skin (erythema), pruritus, pain, and swelling | ✔ | ||
| COMMON | |||
| Upper respiratory tract infections like coughs and cold, pneumonia, cellulitis (skin infection) | ✔ | ||
| Cold sores (oral herpes simplex), blisters, shingles (herpes zoster), skin infection sometimes with fever and chills. Low white blood cell counts, shown by blood tests, high blood lipids (cholesterol levels), headache, dizziness, high blood pressure, mouth ulceration, stomach pain, abnormal liver function tests, rash and itching | ✔ | ||
| Injection site reactions (with subcutaneous use) | ✔ | ||
| In addition, in sJIA: ear infection, chicken pox, gastroenteritis (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), MAS (macrophage activation syndrome – fever, tiredness, headache, confusion, large lymph nodes, liver or spleen) | ✔ | ||
| UNCOMMON | |||
| Diverticulitis (fever, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, stomach pain), red swollen (inflamed) areas in the mouth, high blood lipids (triglyceride levels) and serious allergic reactions | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Pancreatitis: Stomach pain, back pain, nausea, vomiting | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Lung disease: shortness of breath, trouble breathing, cough | ✔ | ✔ | |
| RARE | |||
| Multiple Sclerosis (including blurred vision, loss of vision, eye pain, feeling dizzy, or numbness, weakness or tingling in the face, arms or legs) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Drug-induced liver injury (loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, itching, dark urine, confusion, abdominal swelling and/or pain in the upper-right side of the stomach) | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes) | ✔ | ✔ | |
Very common: at least 1 in 10 patients; Common: at least 1 in 100 and less than 1 in 10 patients; Uncommon: at least 1 in 1,000 and less than 1 in 100 patients; Rare: at least 1 in 10,000 and less than 1 in 1,000 patients.
If you have a troublesome symptom or side effect that is not listed here or becomes bad enough to interfere with your daily activities, tell your healthcare professional.
How to store
Your ACTEMRA vials should be stored under refrigeration (2-8°) and protected from light. Your
healthcare professional will prepare the solution for intravenous (IV) administration.
Your ACTMERA syringe and autoinjector should be stored in a refrigerator at a temperature of 2-8°C.
Keep the autoinjector in the outer carton in order to protect from light and moisture.
Protect the syringe and autoinjector from freezing and from light. Keep the syringe and autoinjector
dry.
Once removed from the refrigerator, ACTEMRA must be administered within 8 hours and should not be
kept above 30°C. For the autoinjectors, allow the autoinjector to sit at room temperature outside the
box for 45 minutes before use.
Keep out of reach and sight of children.
Reporting side effects
You can report any suspected side effects associated with the use of health products to Health Canada by:
- Visiting the Web page on Adverse Reaction Reporting (https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/medeffect-canada.html) for information on how to report online, by mail or by fax; or
- Calling toll-free at 1-866-234-2345.
NOTE: Contact your health professional if you need information about how to manage your side effects. The Canada Vigilance Program does not provide medical advice.
More information
If you want more information about ACTEMRA:
- Talk to your healthcare professional
- Find the full product monograph that is prepared for healthcare professionals and includes this Patient Medication Information by visiting the Health Canada website: (https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/drugs-health-products/drug-products/drug-product-database.html; the manufacturer’s website www.rochecanada.com, or by calling 1-888-387-7374.
*a measurement called HAQ was used to quantify disability (dressing, grooming, eating, walking,
hygiene, reach, grip, activities)
This leaflet was prepared by Hoffmann-La Roche Limited.
Last Revised October 13, 2022
©Copyright 2010-2022 Hoffmann-La Roche Limited
ACTEMRA®, ACTPen® are registered trademarks of Chugai Seiyaku Kabushiki Kaisha, used
under
license.
Rituxan®, is a registered trade-mark of IDEC Pharmaceuticals Corp. used under license.
All other trade-marks are the property of their respective owners.
Hoffmann-La Roche Limited
Mississauga, ON L5N 5M8
APPENDIX 1 – INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
What is the safe way to handle and dispose of ACTEMRA? If you use ACTEMRA at home, you must throw away pre-filled syringes and autoinjectors in a box that will not let the needles stick through it. This will help protect you and other people from accidental needle sticks. Being stuck by a needle not only hurts, but also can pass diseases on to other people. You can get these special boxes, often called “puncture-resistant containers,” from your doctor or pharmacist. Keep this box out of the reach and sight of children. When the box is full, follow your health care provider’s instructions for throwing it away. Placing used boxes in the household waste should be avoided. For safety reasons, always throw away syringes and autoinjectors promptly and never re-use them.
Pre filled Syringes with Needle Safety Device (PFS with NSD):
The following instructions will help you learn how to use ACTEMRA pre-filled syringes to inject yourself.
It is important to follow these directions carefully. Talk to your health care provider if you have any
concerns about how to use ACTEMRA.
If you are giving this injection to someone else, a health care provider must teach you how to avoid
needle sticks. Being stuck by a needle can pass diseases on to you.
What do I need to know to use my ACTEMRA prefilled syringe safely?
It is important to read, understand and follow these instructions so that you or your caregiver uses the
ACTEMRA syringe correctly. These instructions do not replace training from your health care provider.
Your health care provider should show you how to prepare and inject properly before you use the
ACTEMRA syringe for the first time. Ask your health care provider any questions you may have. Do not
attempt to administer an injection until you are sure that you understand how to use the ACTEMRA
syringe.
Please also read the Package Insert that comes with the ACTEMRA syringe for the most important
information you need to know about the drug. It is important to remain under your healthcare
provider's care while using ACTEMRA.
Intended use
This ACTEMRA syringe is intended to be used by patients or caregivers who have been properly trained.
The syringe has a safety mechanism to prevent accidental needle-stick injuries by automatically
covering the needle after injection. Please do not try to take apart the syringe at any time. The syringe
is for single-use only and is then to be discarded. You will inject the medication every week or every
other week, or as directed by your physician.
Important Information:
- Do not use the syringe if it appears to be damaged
- Do not use if medicine is cloudy, hazy, discolored or contains particles
- Do not try to take apart the syringe at any time
- Do not remove the needle-cap until you are ready to inject
- Do not inject through clothing covering the skin
- Never re-use the same syringe
- Do not touch the syringe trigger fingers as this may damage the syringe
Storage
Keep the ACTEMRA syringe and all medicines out of the reach and sight of children. Always store the
syringe in a refrigerator at a temperature of 2-8°C. Protect the syringe from freezing and from light.
Keep the syringe dry. Once removed from the refrigerator, ACTEMRA must be administered within 8
hours and should not be kept above 30°C.
Pre-filled Syringe parts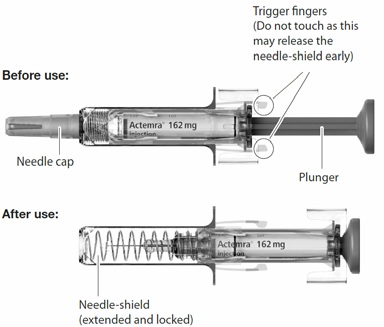
You will need the following to give your injection:
Included in the box:
- Pre-filled Syringe
Not included in the box:
- Alcohol pad
- Sterile cotton ball or gauze
- Puncture-resistant container or sharps container for safe disposal of needle-cap and used syringe
You may need to purchase these.
A place to prepare your supplies:
- Find a well-lit, clean, flat surface such as a table
How to give your injection:
Step 1. Visually check the syringe
- Take the box containing the syringe out of the refrigerator and open the box. Do not touch the trigger fingers on the syringe (see figure above) as this may damage the syringe.
- Remove the syringe from the box and visually examine the syringe, as well as the medicine in the syringe. This is important to ensure that the syringe and medicine are safe to use.
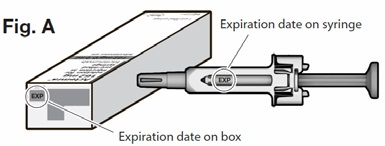
- Check the expiration date on the box and syringe (See Fig. A below) to make sure that it has not
passed (expired). Do not use the syringe if the expiration date has passed. This is important to
ensure that the syringe and medicine are safe to use.
If any of the following are present do NOT use the syringe; set it aside and contact your pharmacist or other healthcare professional:
- the medicine is cloudy
- the medicine contains particles
- the medicine is any color besides colorless to yellowish
- any part of the syringe appears to be damaged
Step 2. Allow the syringe to adjust to room temperature
- Do not remove the needle-cap on your syringe until Step 5.
- Place the syringe on a clean flat surface and allow the syringe to come to room temperature for about 25-30 minutes to warm up. Not allowing the syringe to come to room temperature could result in an uncomfortable injection and it may be difficult to depress the plunger.
- Do not warm up the syringe in any other way.
Step 3. Clean your hands
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
Step 4. Choose and prepare an injection site
- The recommended injection sites are the front and middle of your thighs and the lower part of the abdomen below the navel (belly button) except for the five centimeter area directly around the navel. (See Fig. B below)
- If a caregiver is giving the injection, the outer area of the upper arms may also be used. (See
Fig. B)
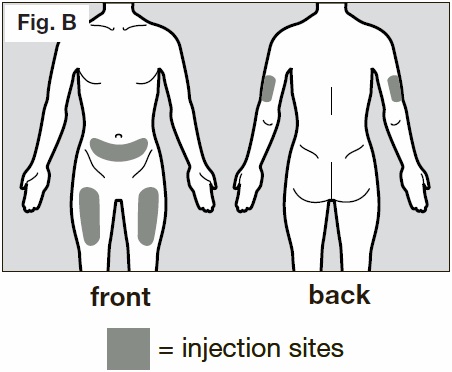
- You should use a different place each time you give yourself an injection, at least three centimeters from the area you used for your previous injection.
- Do not inject into areas that could be bothered by a belt or waistband. Do not inject into moles, scars, bruises, or areas where the skin is tender, red, hard or not intact.
- Clean the chosen injection site area using the alcohol pad (See Fig. C below), to reduce the risk
of infection.
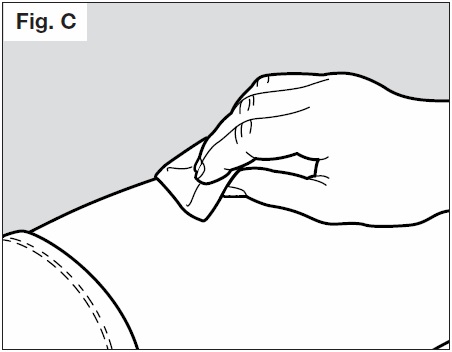
- Let the skin dry for approximately 10 seconds.
- Be sure not to touch the cleaned area prior to the injection. Do not fan or blow on the clean area.
Step 5. Remove needle-cap
- Do not hold the syringe by the plunger while removing the needle-cap.
- Hold the needle-shield of the syringe firmly with one hand and pull off the needle-cap with the
other hand. (See Fig. D below) If you cannot remove the needle cap you should request the
help of a caregiver or contact your health care provider.
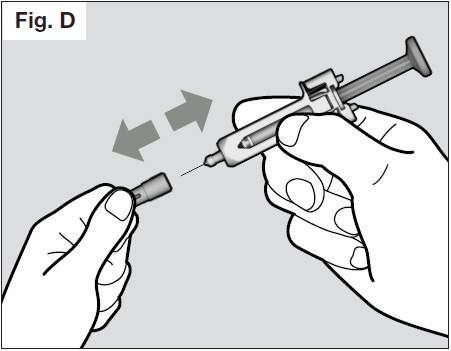
- Do not touch the needle or let it touch any surface.
- You may see a drop of liquid at the end of the needle. This is normal.
- Throw away the needle-cap in the puncture resistant container or sharps container.
- NOTE: Once the needle-cap is removed, the syringe should be used immediately. If it is not used within 5 minutes, the syringe should be disposed of in the puncture resistant container or sharps container and a new syringe should be used.
- Never reattach the needle-cap after removal.
Step 6. Give the injection
- Hold the syringe comfortably in your hand.
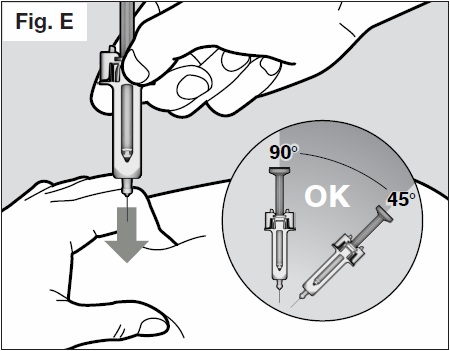
- To be sure the needle can be inserted correctly under the skin, pinch a fold of loose skin at the clean injection site with your free hand. Pinching the skin is important to ensure that you inject under the skin (into fatty tissue) but not any deeper (into muscle). Injection into muscle could result in an uncomfortable injection.
- Do not hold or push on the plunger while inserting the needle into the skin.
- Insert the needle all the way into the pinched skin at an angle between 45° to 90° with a quick,
firm action. (See Fig. E below).
- Then keep the syringe in position and let go of the pinch of skin.
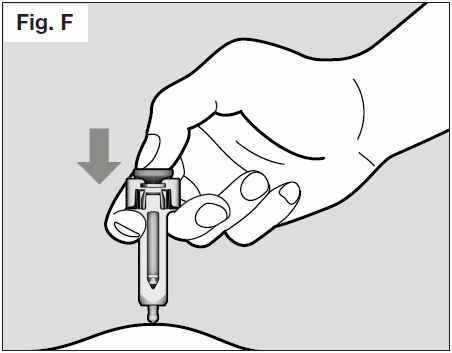
- Slowly inject all of the medicine by gently pushing the plunger all the way down. (See Fig. F).
You must press the plunger all the way down to ensure that you get the full dose of medication
and to ensure the trigger fingers are completely pushed to the side. If the plunger is not fully
depressed the needle shield will not extend to cover the needle when it is removed. If the
needle is not covered proceed carefully, and place the syringe into the puncture resistant
container to avoid injury with the needle.
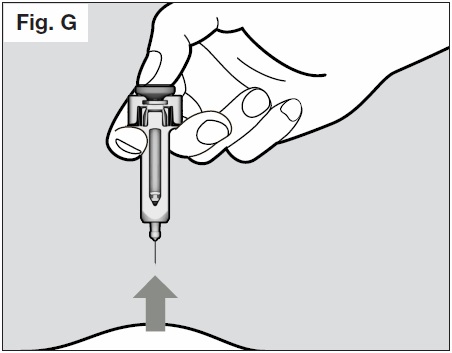
- Once the plunger is pushed all the way down, keep pressing down on the plunger to be sure all of the medicine is injected before taking the needle out of the skin.
- Keep pressing down on the plunger while you take the needle out of the skin at the same angle
as inserted. (See Fig. G below)
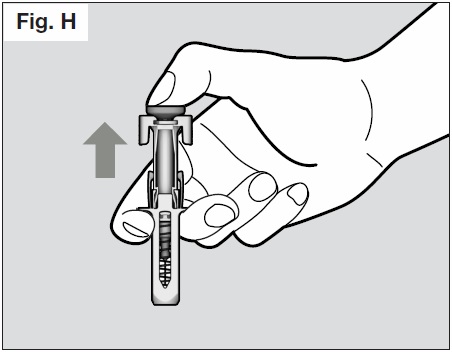
- Once the needle is removed completely from the skin, you can release the plunger, allowing
the needle-shield to protect the needle. (See Fig. H below)
- If you see drops of blood at the injection site, you can press a sterile cotton ball or gauze over the injection site for approximately 10 seconds.
- Do not rub the injection site.
It is important to choose the correct angle to ensure the medication is delivered under the skin (into fatty tissue), otherwise the injection could be painful and the medication may not work.
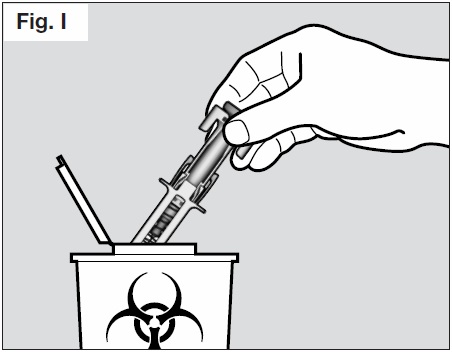
Step 7. Dispose of the syringe
- Do not try to re-cap your syringe.
- Throw away used syringes in a puncture-resistant container or sharps container. (See Fig. I
below).
ACTEMRA autoinjector
The following instructions will help you learn how to use ACTEMRA autoinjector. It is important to
follow these directions carefully. Talk to your health care provider if you have any concerns about how
to use ACTEMRA.
If you are giving this injection to someone else, a health care provider must teach you how to avoid
needle sticks. Being stuck by a needle can pass diseases on to you.
What do I need to know to use my ACTEMRA autoinjector?
It is important to read, understand and follow these instructions so that you or your caregiver uses the
ACTEMRA autoinjector correctly. These instructions do not replace training from your health care
provider. Your health care provider should show you how to prepare and inject properly before you use
the ACTEMRA autoinjector for the first time. Ask your health care provider any questions you may
have. Do not attempt to administer an injection until you are sure that you understand how to use the
ACTEMRA autoinjector.
Intended use
This ACTEMRA autoinjector is intended to be used by patients or caregivers who have been properly
instructed. The autoinjector has a safety mechanism to prevent accidental needle-stick injuries by
automatically covering the needle after injection. Please do not try to open the autoinjector or take it
apart at any time. The autoinjector is for single-use only and is then to be discarded. You will inject the
medication every week, or as directed by your physician.
Important Information:
- Do not use if the autoinjector appears to be damaged
- Do not use if medicine is cloudy, hazy, discolored or contains particles
- Do not remove the autoinjector cap until you are ready to inject the autoinjector
- Do not try to take apart the autoinjector at any time
- Do not reuse the same autoinjector
- Do not use the autoinjector through clothing.
- Do not leave the autoinjector unattended
Keep the ACTEMRA autoinjector and all medicines out of the reach and sight of children. Always store
the autoinjector in a refrigerator at a temperature of 2–8 ºC. Protect the autoinjector from freezing and
from light. Keep the autoinjector dry. Allow the autoinjector to sit at room temperate outside the box
for 45 minutes before use.
ACTEMRA Autoinjector parts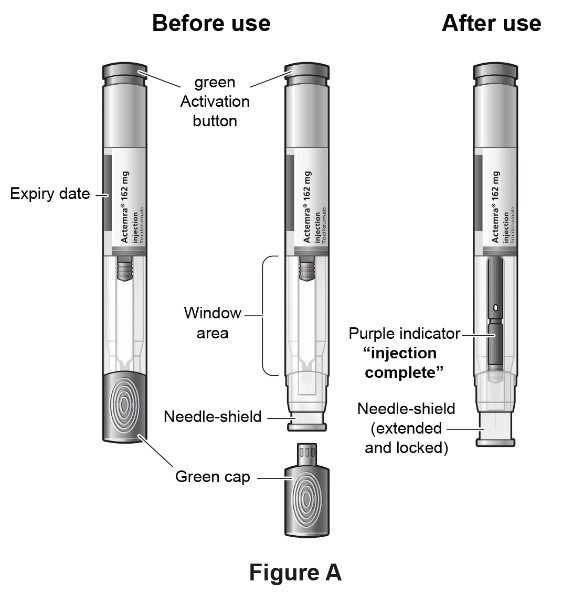
You will need the following to give your injection:
Included in the pack:
- Autoinjector
Not included in the pack:
- Alcohol pad
- Sterile cotton ball or gauze
- Puncture-resistant container or sharps container for safe disposal of the green cap and used autoinjector.
You may need to purchase these.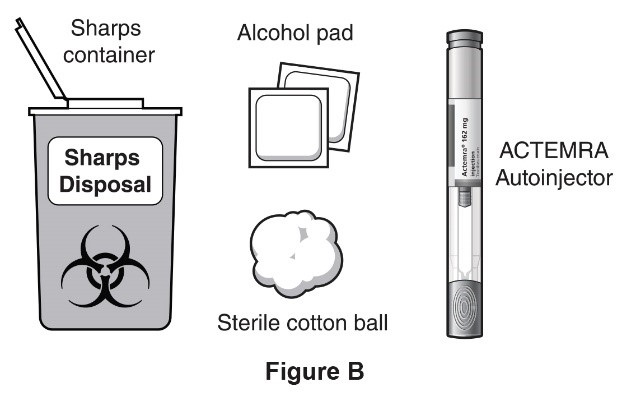
A place to prepare your supplies:
- Find a comfortable space with a clean, flat, working surface.
How to give your injection:
Step 1. Visually check the autoinjector
- Take the box containing the autoinjector out of the refrigerator.
- If you are opening the box for the first time, check to make sure that it is properly sealed. Do not use the autoinjector if the box looks like it has already been opened.
- Check that the autoinjector box is not damaged. Do not use autoinjector if the box looks damaged.
- Check the expiration date on the autoinjector box. Do not use the autoinjector if the expiration date has passed because it may not be safe to use.
- Open the box, and remove 1 single-use autoinjector from the box.
- Return any remaining autoinjector in the box to the refrigerator.
- Check the expiration date on the autoinjector (See Figure A). Do not use it if the expiration date has passed because it may not be safe to use. If the expiration date has passed, safely dispose of the autoinjector in a sharps container and get a new one.
- Check the autoinjector to make sure it is not damaged. Do not use the autoinjector if it appears to be damaged or if you have accidentally dropped the autoinjector.
- Place the autoinjector on a clean, flat surface and let the autoinjector warm up for 45 minutes to allow it to reach room temperature. If the autoinjector does not reach room temperature, this could cause your injection to feel uncomfortable and it could take longer to inject.
- Do not speed up the warming process in any way, such as using the microwave or placing autoinjector in warm water.
- Do not leave the autoinjector to warm up in direct sunlight.
- Do not remove the green cap while allowing your autoinjector to reach room temperature.
- Hold your autoinjector with the green cap pointing down (See Figure C).
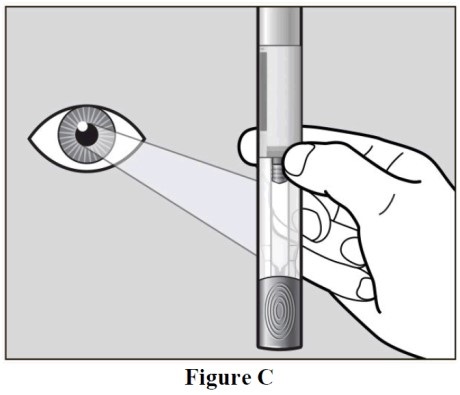
- Look in the clear Window area. Check the liquid in the autoinjector (See Figure C).
- It should be clear and colorless to pale yellow.
- Do not inject autoinjector if the liquid is cloudy, discolored, or has lumps or particles in it because it may not be safe to use.
- If the liquid is cloudy, discolored or has lumps or particles, safely dispose of the autoinjector in a sharps container and get a new one.
- Wash your hands well with soap and water.
Step 2. Choose and Prepare an Injection Site
Choose an Injection Site
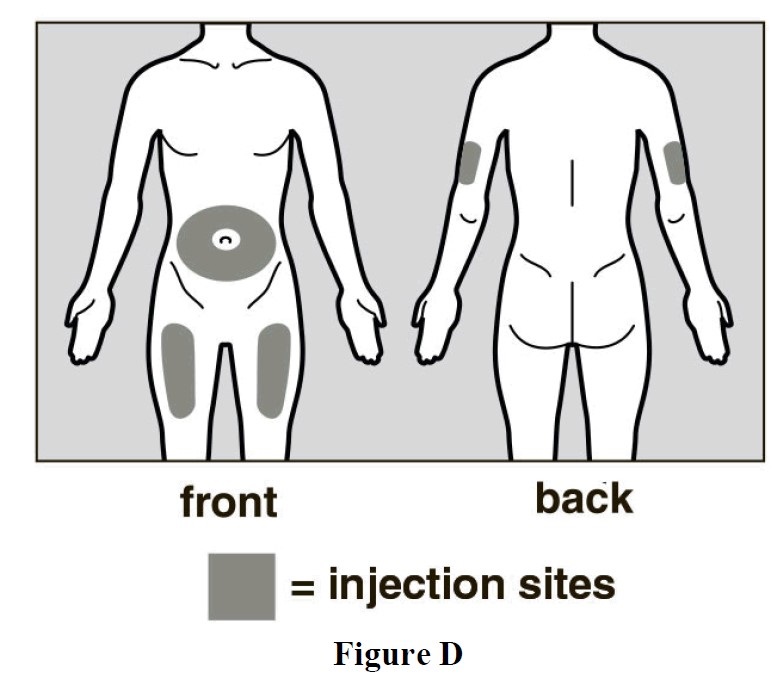
- The front of your thigh or your abdomen except for the 2-inch (5cm) area around your navel are the recommended injection sites (See Figure D).
- The outer area of the upper arms may also be used only if the injection is being given by a caregiver. Do not attempt to use the upper arm area by yourself (See Figure D).
Rotate Injection Site
- Choose a different injection site for each new injection at least 1 inch (2.5cm) from the last area you injected.
- Do not inject into moles, scars, bruises, or areas where the skin is tender, red, hard or not
intact.
Prepare the Injection Site
- Wipe the injection site with an alcohol pad in a circular motion and let it air dry to reduce the chance of getting an infection. Do not touch the injection site again before giving the injection.
- Do not fan or blow on the clean area.
Step 3. Inject autoinjector
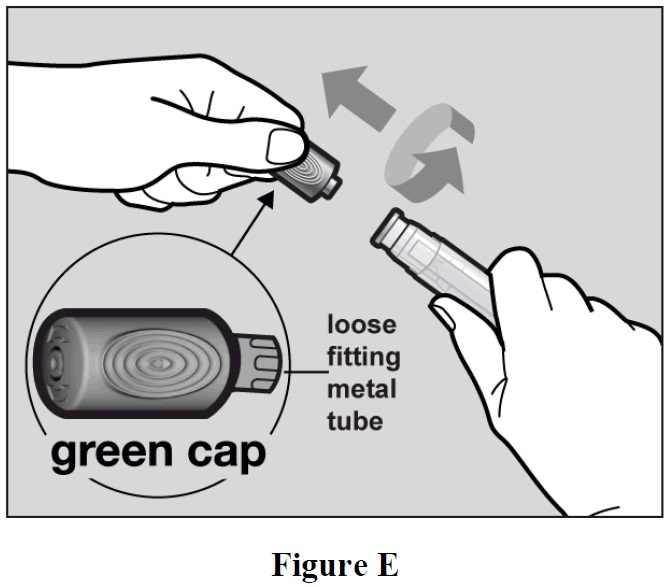
- Hold the autoinjector firmly with one hand. Twist and pull off the green cap with the other hand (See Figure E). The green cap contains a loose fitting metal tube.
- If you cannot remove the green cap you should ask a caregiver for help or contact your
healthcare provider.
Important: Do not touch the needle shield which is located at the tip of the Autoinjector below the Window area (see Figure A), to avoid accidental needle stick injury.
- Throw away the green cap in a sharps container.
- After you remove the green cap, the autoinjector is ready for use. If the autoinjector is not used within 3 minutes of the cap removal, the autoinjector should be disposed of in the sharps container and a new autoinjector should be used.
- Never reattach the green cap after removal.
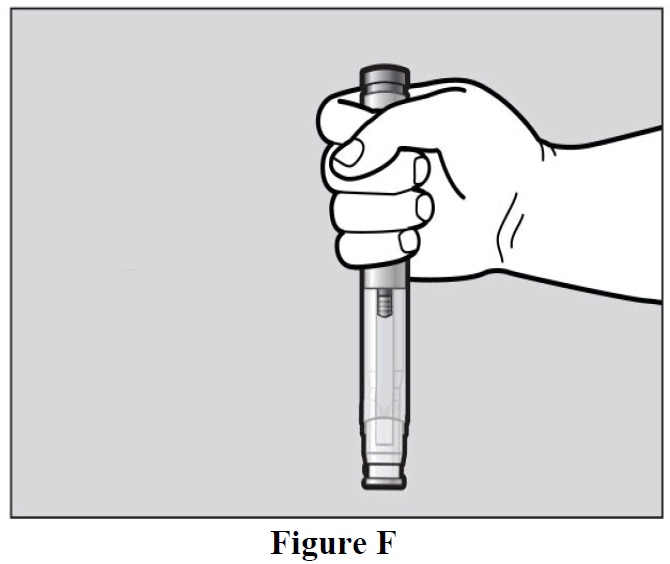
- Hold the autoinjector comfortably in 1 hand by the upper part, so that you can see the window
area of the autoinjector (See Figure F).
- Use your other hand to gently pinch the area of skin you cleaned, to prepare a firm injection site (See Figure G). The autoinjector requires a firm injection site to properly activate.
- Pinching the skin is important to make sure that you inject under the skin (into fatty tissue) but
not any deeper (into muscle). Injection into muscle could cause the injection to feel
uncomfortable.
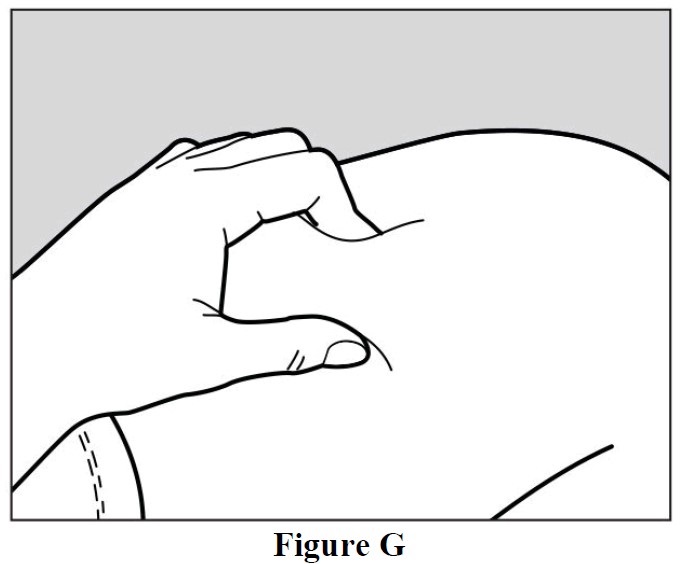
- Do not press the green activation button yet.
- Place the needle-shield of the autoinjector against your pinched skin at a 90° angle (See Figure H).
- It is important to use the correct angle to make sure the medicine is delivered under the skin
(into fatty tissue), or the injection could be painful and the medicine may not work.
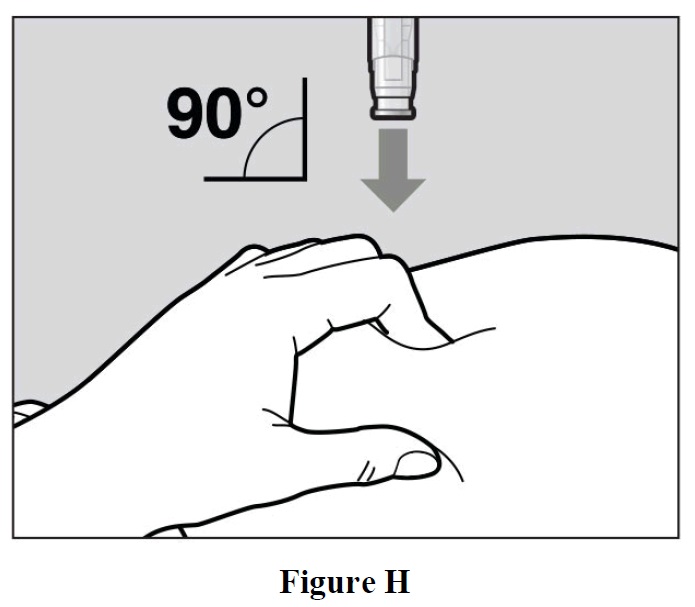
- To use the autoinjector, you first have to unlock the green Activation button.
- To unlock it, press the autoinjector firmly against your pinched skin until the needle-shield is
completely pushed in (See Figure I).
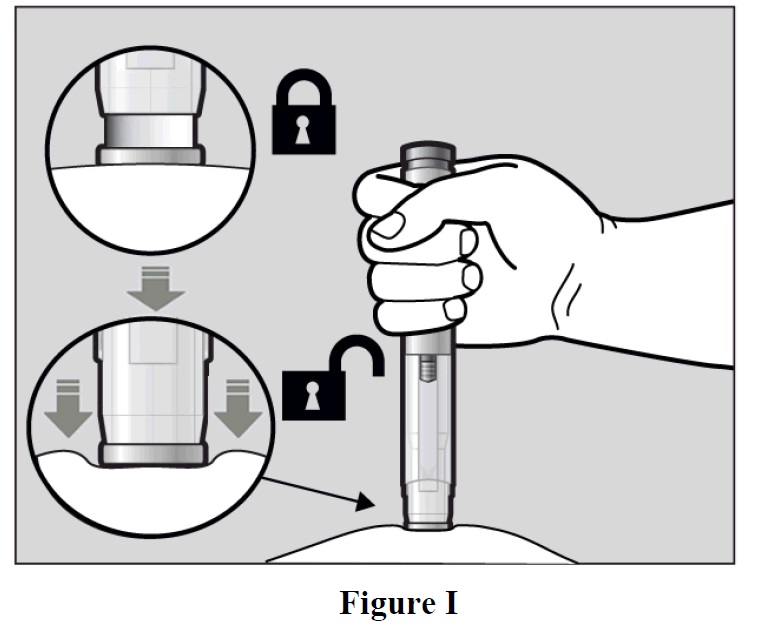
- Continue to keep the needle-shield pushed in.
- If you don’t keep the needle-shield completely pushed against the skin, the green Activation button will not work.
- Continue to pinch the skin while you keep the autoinjector in place.
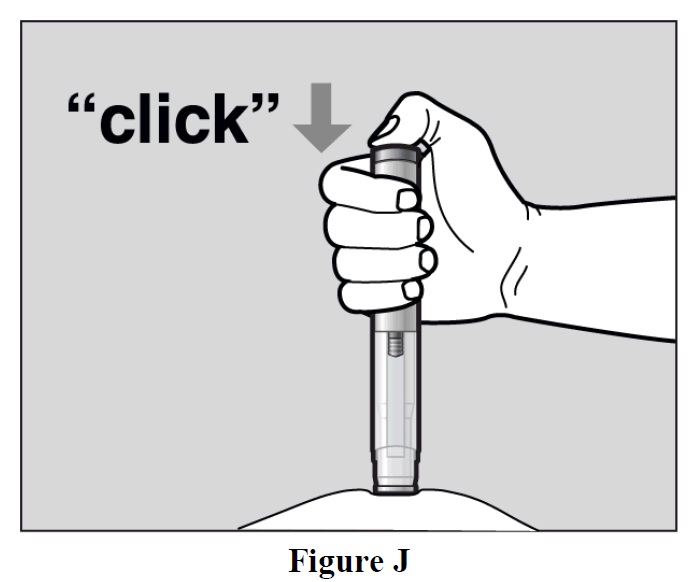
- Press the green Activation button to start the injection. A “click” sound indicates the start of
the injection. Keep the green button pressed in and continue holding the autoinjector pressed
firmly against your skin (See Figure J). If you cannot start the injection you should ask for help
from a caregiver or contact your healthcare provider.
- The purple indicator will move along the Window area during the injection (See Figure K).
- Watch the purple indicator until it stops moving to be sure the full dose of medication is
injected.
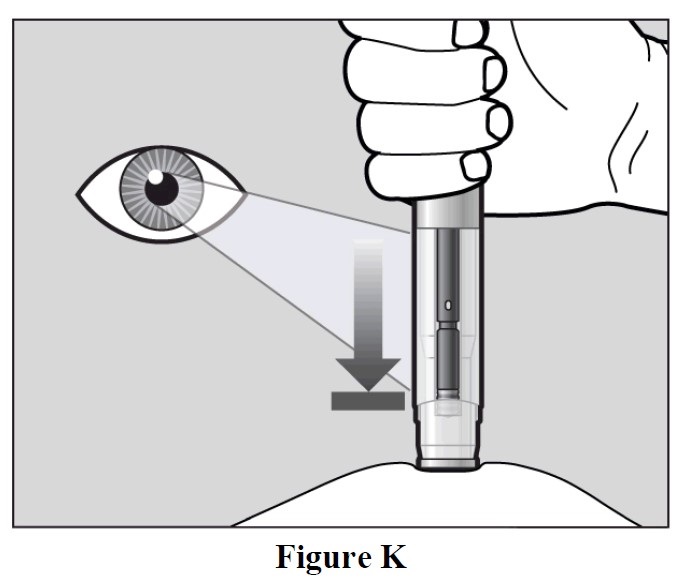
- The injection may take up to 10 seconds.
- You may hear a second “click” during the injection but you should continue to hold the autoinjector firmly against your skin until the purple indicator stops moving.
- When the purple indicator has stopped moving, release the green button. Lift the autoinjector
straight off of the injection site at a 90° angle to remove the needle from the skin. The needle
shield will then move out and lock into place covering the needle (See Figure L).
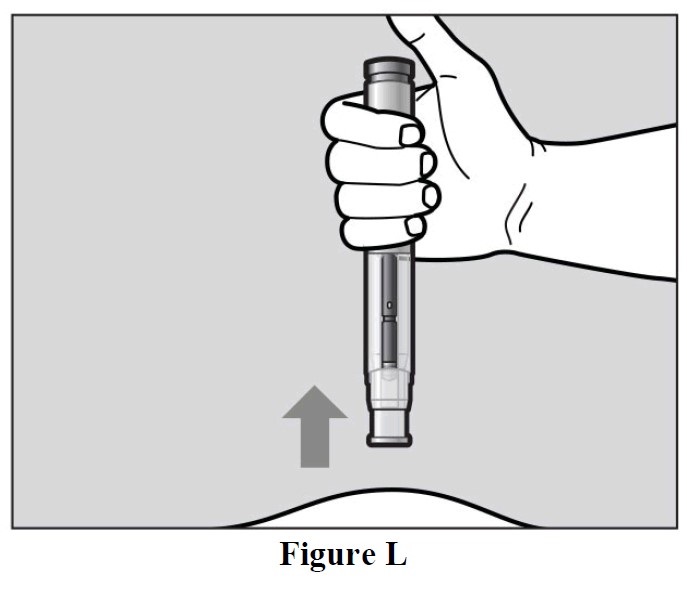
- Check the Window area to see that it is filled with the purple indicator (See Figure L).
- If the Window area is not filled by the purple indicator, then:
- The needle-shield may not have locked. Do not touch the needle-shield of the autoinjector, because you may stick yourself with the needle. If the needle is not covered, carefully place the autoinjector into the sharps container to avoid any injury with the needle.
- You may not have received your full dose of ACTEMRA. Do not try to re-use the autoinjector. Do not repeat the injection with another autoinjector. Call your healthcare provider for help.
After the Injection
- There may be a little bleeding at the injection site. You can press a cotton ball or gauze over the injection site.
- Do not rub the injection site.
- If needed, you may cover the injection site with a small bandage.
Step 4. Dispose of the autoinjector
- The ACTEMRA autoinjector should not be reused.
- Put the used autoinjector into your sharps container (see “How do I dispose of used autoinjector?”)
- Do not put the cap back on the autoinjector.
- If your injection is given by another person, this person must also be careful when removing the autoinjector and disposing of it to prevent accidental needle stick injury and passing infection.
- Put your used ACTEMRA autoinjector and green cap in a sharps disposal container right away after use (See Figure M).
- Do not throw away (dispose of) the autoinjector and the green cap in your household trash and
do not recycle them.

- Dispose of the full container as instructed by your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
- Always keep the puncture-resistant container out of the sight and reach of children.
- Write the date, time, and specific part of your body where you injected yourself. It may also be helpful to write any questions or concerns about the injection so you can ask your healthcare provider.
How do I dispose of used autoinjectors?
Keep the ACTEMRA autoinjector and disposal container out of the reach and sight of
children.
Record your Injection
If you have any concerns or questions about your autoinjector, contact your healthcare provider or pharmacist for assistance.
Report a problem on this page
- Date modified: